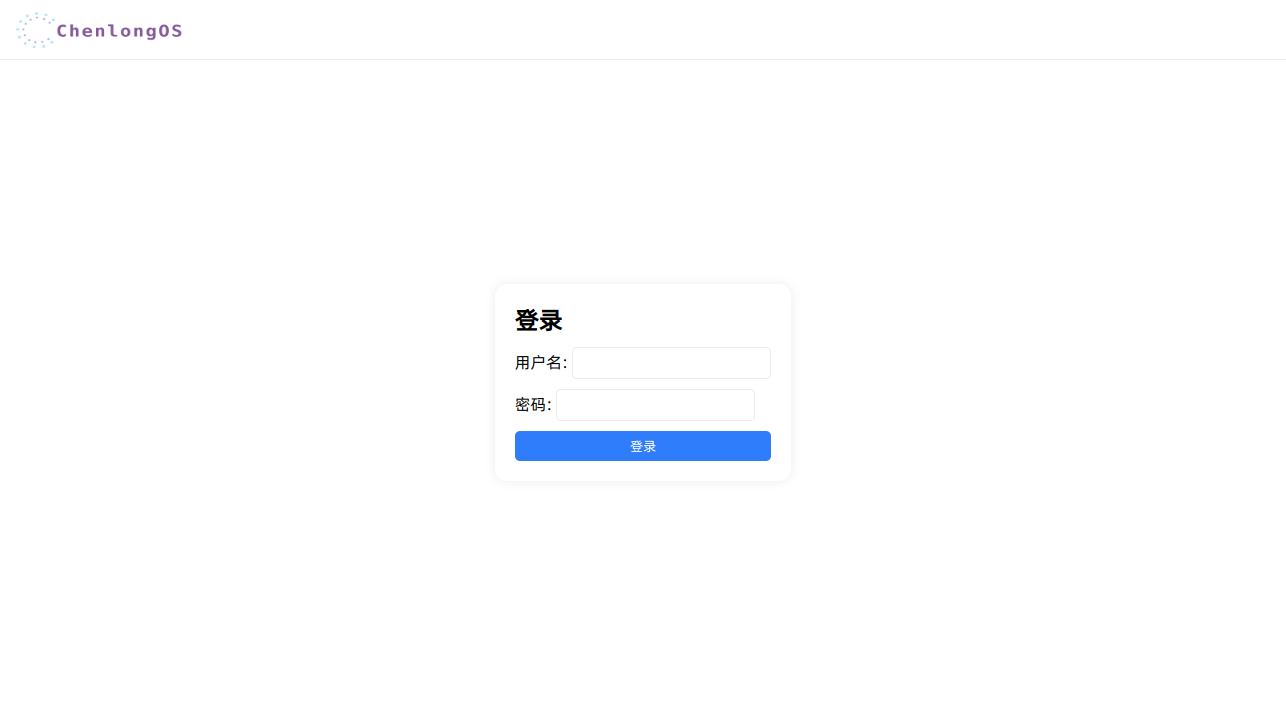
httpserver 代码分析#
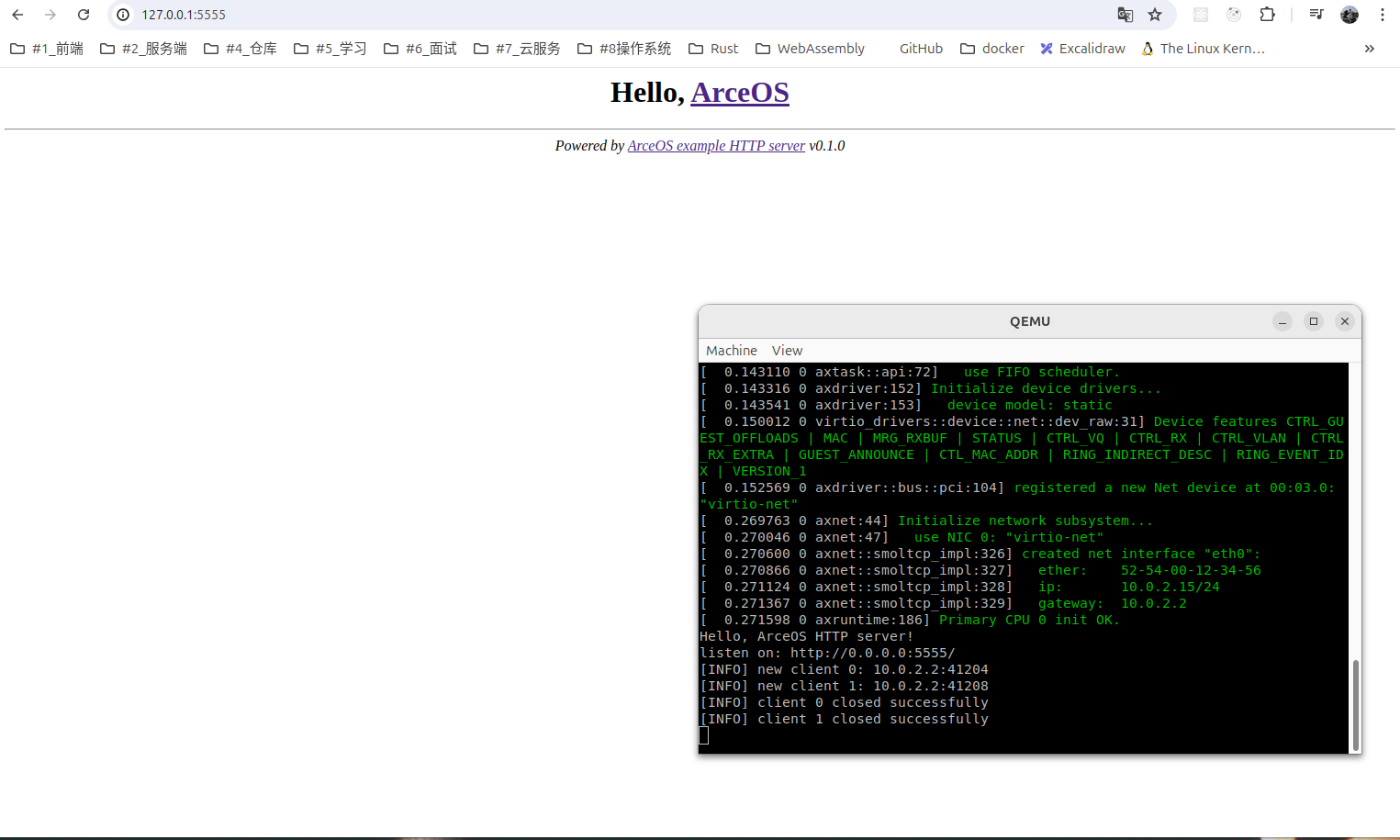
运行 httpserver 查看效果#
运行命令
make A=apps/net/httpserver ARCH=x86_64 GRAPHIC=on BLK=y NET=y LOG=info run效果图:
替换以上代码中固定的内容 ,采用 fs 的 read 函数 读取 index.html 内容
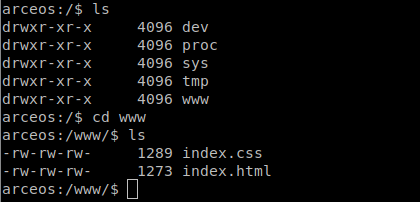
当前根目录下的文件结构如下:
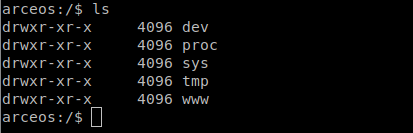
挂载/www、/index.html和/index.css#
在axfs模块下的 fs 文件夹下的root.rs,将/www文件挂载到/文件夹下。
#[cfg(feature = "ramfs")]
root_dir
.mount("/www", mounts::ramfs().unwrap())
.expect("failed to mount ramfs at /www");找到axfs模块下的 fs 文件夹下的mounts.rs文件,将/index.html文件夹挂载到/www文件夹下。
#[cfg(feature = "ramfs")]
pub(crate) fn ramfs() -> VfsResult<Arc<fs::ramfs::RamFileSystem>> {
let wwwfs = fs::ramfs::RamFileSystem::new();
let www_root = wwwfs.root_dir();
www_root.create("index.html", VfsNodeType::File)?;
www_root.create("index.css", VfsNodeType::File)?;
let html_file = www_root.clone().lookup("./index.html")?;
let css_file = www_root.clone().lookup("./index.css")?;
html_file.write_at(0, r#"
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">
<title>Hello, ArceOS</title>
<link href="./index.css" rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" />
</head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<div class="header">
<img class="logo" src="https://chenlongos.cn/images/black-logo.png" alt="" />
</div>
<div class="content">
<div class="login-form">
<h2>登录</h2>
<form action="/login" method="post">
<label for="name">用户名:</label>
<input class="input" type="text" id="name" name="name" required>
<br>
<label for="password">密码:</label>
<input class="input" type="password" id="password" name="password" required>
<br>
<input class="btn" type="submit" value="登录">
</form>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
"#.as_bytes())?;
css_file.write_at(0, r#"
*{
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
.container {
width: 100%;
min-height: 100vh;
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
}
.container .header {
box-sizing: border-box;
height: 60px;
display: flex;
align-items: center;
border-bottom: 1px solid #00000014;
}
.container .header .logo {
width: 200px;
height: 40px;
}
.container .content {
flex-grow: 1;
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
}
.container .content .login-form {
padding: 20px;
box-sizing: border-box;
box-shadow: 0 0 10px #00000014;
border-radius: 12px;
}
.container .content .login-form .input {
height: 30px;
border: 1px solid #00000014;
border-radius: 5px;
padding: 0 10px;
margin-top: 10px;
}
.container .content .login-form .btn {
width: 100%;
height: 30px;
background-color: #007bff;
color: #fff;
border: none;
border-radius: 5px;
cursor: pointer;
margin-top: 10px;
}
.container .content .login-form .btn:hover {
background-color: #0056b3;
}
"#.as_bytes())?;
Ok(Arc::new(wwwfs))
}通过硬编码的方式,直接将 index.html 和 index.css 的内容写入到文件中。
根目录下已绑定www文件夹,在www文件夹中我们成功的挂载了index.css和index.html
使用cat指令指令查看index.html文件内容
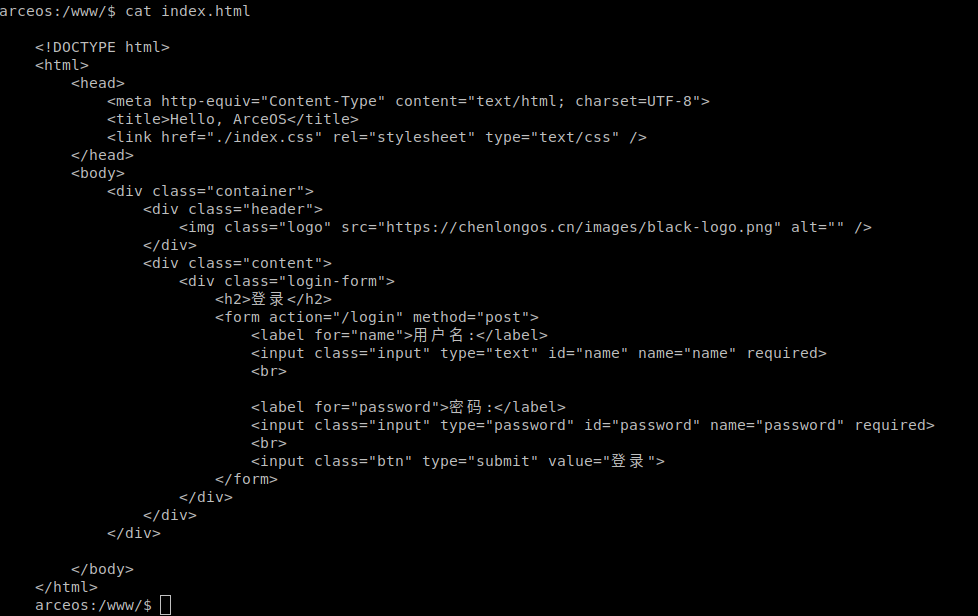
运行与 httpserver 隔离的硬编码 html 文件#
效果如下:
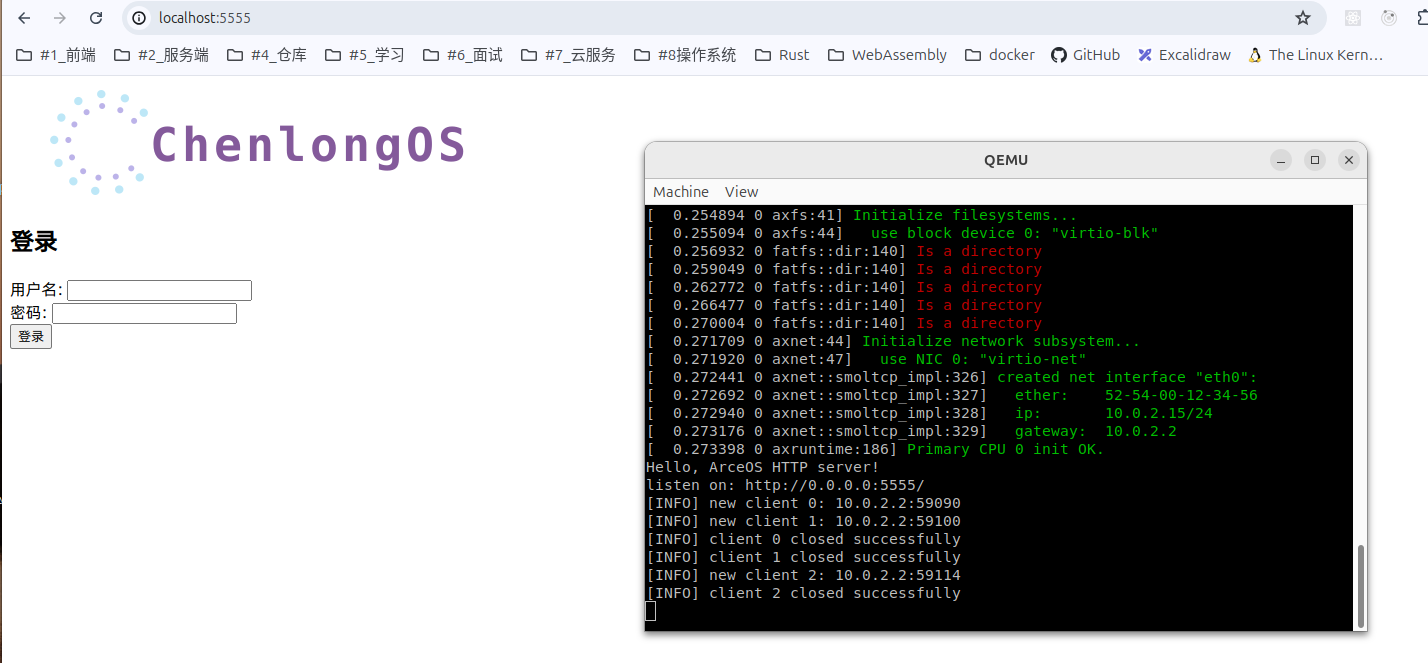
我们发现我们写的 html 文件被正常解析了,但是我们的 css 文件并没有被加载,这是因为我们的 css 文件并没有被加载。
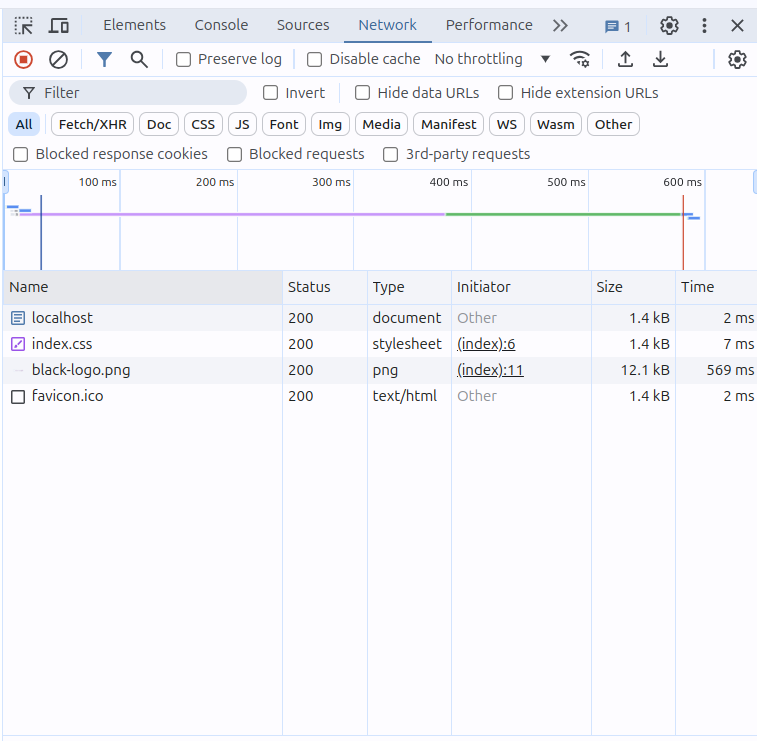
我们打开浏览器的控制台,查看请求的 css 文件路径,发现请求确实是发出去了,并且我们也接受到了 css 文件,那为什么没有解析呢?
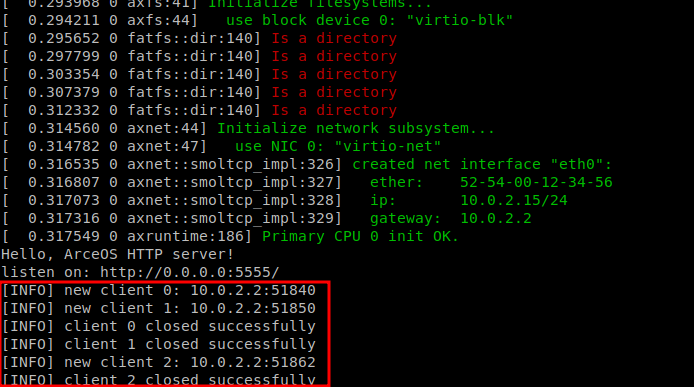
我们进一步查看,发现我们 httpserver 返回的响应头中的Content-Type字段被设置成text/html,浏览器将它解析成了 text/html,所以我们的 css 文件没有被解析。
因此我们需要将Content-Type字段设置成text/css,这样浏览器就会将其解析成 css 文件。
找到httpserver应用下的main.rs我们可以看到目前确实已经将content-type字段硬编码为text/html;
macro_rules! header {
() => {
"\
HTTP/1.1 200 OK\r\n\
Content-Type: text/html\r\n\
Content-Length: {}\r\n\
Connection: close\r\n\
\r\n\
{}"
};
}接下来我们就需要将content-type字段设置成动态的,我们可以通过文件的后缀名来判断文件的类型,然后设置content-type字段。
封装TcpStream,将 TcpStream 流解析成我们自己定义的HttpRequest。
fn http_server(mut stream: TcpStream) -> io::Result<()> {
let mut buf = [0u8; 4096];
stream.read(&mut buf)?;
let request_str = String::from_utf8_lossy(&buf);
let request = HttpRequest::new(&request_str);
let method = request.get_method();
info!("Method: {}", method);
let version = request.get_version();
info!("Version: {}", version);
let mut uri = request.get_path();
info!("URI:{}", uri);
let content_type = resolve_content_type(uri);
info!("Content-Type: {} ", content_type);
if uri == "/" {
uri = "/index.html";
}
let content = fs::read(format!("/www/{}", uri).as_str())?;
let content = unsafe { core::str::from_utf8_unchecked(&content) };
let response = format!(header!(), content_type , content.len(), content);
stream.write_all(response.as_bytes())?;
Ok(())
}
// httpserver/http/request.rs
use core::str::Lines;
use std::string::String;
use std::string::ToString;
use std::vec::Vec;
#[derive(Debug,Clone)]
pub struct HttpRequest {
pub method: String,
pub path: String,
pub version: String,
pub headers: Vec<RequestHeader>
}
#[derive(Debug, Clone)]
pub struct RequestHeader {
pub key: String,
pub value: String,
}
impl RequestHeader {
pub fn new(key: &str, value: &str) -> RequestHeader {
RequestHeader {
key: key.to_string(),
value: value.to_string(),
}
}
}
impl HttpRequest {
pub fn new(request: &str) -> HttpRequest {
let mut method = String::new();
let mut path = String::new();
let mut version = String::new();
let mut lines = request.lines();
let first_line = lines.next().unwrap();
let mut parts = first_line.split_whitespace();
method.push_str(parts.next().unwrap());
path.push_str(parts.next().unwrap());
version.push_str(parts.next().unwrap());
let headers = Self::parse_headers(&mut lines);
HttpRequest {
method,
path,
version,
headers,
}
}
fn parse_headers(lines: &mut Lines) -> Vec<RequestHeader> {
let mut headers = Vec::new();
for line in lines {
let line = line.trim();
if line.is_empty() {
// Stop parsing headers if we encounter an empty line
break;
}
let mut header_parts = line.splitn(2, ": ");
if let (Some(key), Some(value)) = (header_parts.next(), header_parts.next()) {
headers.push(RequestHeader::new(key, value));
}
}
headers
}
pub fn get_path(&self) -> &str {
&self.path
}
pub fn get_method(&self) -> &str {
&self.method
}
pub fn get_version(&self) -> &str {
&self.version
}
pub fn get_headers(&self) -> Vec<RequestHeader> {
self.headers.clone()
}
pub fn get_headers_value(&self, key: &str) -> &str {
for header in &self.headers {
if header.key == key {
return header.value.as_str();
}
}
""
}
}
// httpserver/src/http/mod.rs
mod request;
mod response;
pub use request::HttpRequest;
pub fn resolve_content_type(uri: &str) -> &str {
let content_type = match uri {
_ if uri == "/" => "text/html",
_ if uri.ends_with(".ico") => "text/html",
_ if uri.ends_with(".html") => "text/html",
_ if uri.ends_with(".css") => "text/css",
_ if uri.ends_with(".js") => "application/javascript",
_ if uri.ends_with(".png") => "image/png",
_ if uri.ends_with(".jpg") => "image/jpeg",
_ if uri.ends_with(".jpeg") => "image/jpeg",
_ if uri.ends_with(".gif") => "image/gif",
_ if uri.ends_with(".svg") => "image/svg+xml",
_ => "text/plain",
};
content_type
}运行效果如下: